2/11/24About 1 min
I Problem
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing nqueens on an n x n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle. You may return the answer in any order.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where 'Q' and '.' both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
Example 1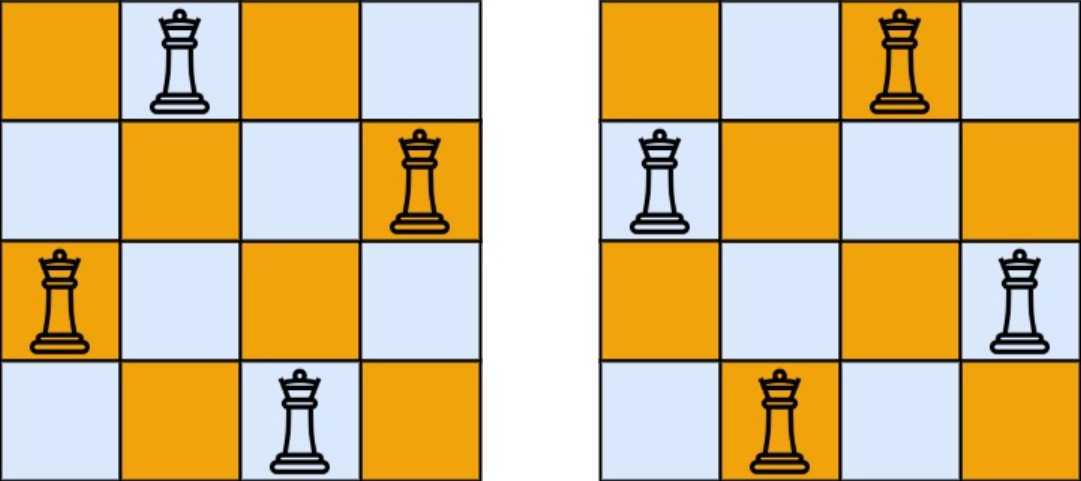
Input: n = 4
Output: [[".Q..", "...Q", "Q...", "..Q."],["..Q.", "Q...", "...Q", ".Q.."]]
Explanation: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above.
Example 2
Input: n = 1
Output: [["Q"]]
Constraints
1 <= n <= 9
Related Topics
- Array
- Backtracking
II Solution
Approach 1: Backtracking
Rust
pub fn solve_n_queens(n: i32) -> Vec<Vec<String>> {
const DFS: fn(i32, i32, &mut Vec<(i32, i32)>, &mut Vec<Vec<String>>) =
|row, len, pos, res| {
if row == len {
let ans = pos
.iter()
.map(|&(_, col)| {
(0..len).into_iter().fold(
String::with_capacity(len as usize),
|mut str, c| {
if c == col {
str.push('Q');
} else {
str.push('.');
}
str
},
)
})
.collect::<Vec<_>>();
res.push(ans);
return;
}
for col in 0..len {
if pos.iter().any(|&(r, c)| {
// Same column
if col == c {
return true;
}
let slope = (row - r) as f64 / (col - c) as f64;
// Same diagonal
slope == 1.0 || slope == -1.0
}) {
continue;
}
pos.push((row, col));
DFS(row + 1, len, pos, res);
pos.pop();
}
};
let mut res = vec![];
DFS(0, n, &mut vec![], &mut res);
res
}Java
@FunctionalInterface
interface QuadrConsumer<A, B, C, D> {
void accept(A a, B b, C c, D d);
}
QuadrConsumer<Integer, Integer, List<int[]>, List<List<String>>> dfs =
(row, len, pos, res) -> {
if (Objects.equals(row, len)) {
List<String> ans = pos.stream().map(p -> {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(len);
for (int c = 0; c < len; c++) {
if (c == p[1]) {
s.append('Q');
} else {
s.append('.');
}
}
return s.toString();
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
res.add(ans);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < len; col++) {
int finalCol = col;
if (pos.stream().anyMatch(p -> {
// Same column
if (p[1] == finalCol) {
return true;
}
double slope = ((double) (row - p[0])) / (finalCol - p[1]);
// Same diagonal
return slope == 1 || slope == -1;
})) {
continue;
}
pos.addLast(new int[]{row, col});
this.dfs.accept(row + 1, len, pos, res);
pos.removeLast();
}
};
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
this.dfs.accept(0, n, new ArrayList<>(), res);
return res;
}