10/24/23About 3 min
I Problem
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nᵗʰ node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1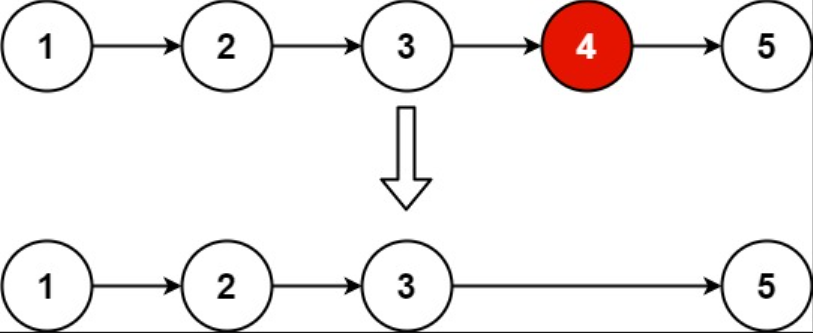
Input: head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], n = 2
Output: [1, 2, 3, 5]
Example 2
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3
Input: head = [1, 2], n = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the list is sz
- 1 <= sz <= 30
- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
- 1 <= n <= sz
Follow up
Could you do this in one pass?
Related Topics
- Linked List
- Two Pointers
II Solution
ListNode(Rust)
#[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
pub struct ListNode {
pub val: i32,
pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
}
impl ListNode {
#[inline]
fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
ListNode { next: None, val }
}
}ListNode(Java)
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode() {}
public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}Approach 1: Calculate Length of Linked List
Rust
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
///
/// Space Complexity: O(1)
pub fn remove_nth_from_end(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, n: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
// calculate the len of linked list
let mut counter = head.as_ref();
let mut len = 0;
while let Some(curr) = counter {
len += 1;
counter = curr.next.as_ref();
}
let mut dummy = ListNode::new(-1);
dummy.next = head;
let mut p = &mut dummy;
// move p to the previous node of to be deleted node
for _ in 0..(len - n) {
p = p.next.as_mut().unwrap();
}
if let Some(mut to_be_del) = p.next.take() {
p.next = to_be_del.next.take();
}
dummy.next
}Java
/**
* Time Complexity: O(n)
* Space Complexity: O(1)
*/
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// calculate the len of linked list
int len = 0;
for (ListNode p = head; p != null; ++len) {
p = p.next;
}
// move p to the previous node of to be deleted node
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode p = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < len - n; i++) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = p.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}Approach 2: Use Stack
Rust
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
///
/// Space Complexity: O(n)
pub fn remove_nth_from_end(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, n: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut stack = vec![];
while let Some(mut curr) = head {
head = curr.next.take();
stack.push(curr);
}
let mut i = 0;
let mut head = None;
while let Some(mut curr) = stack.pop() {
i += 1;
if i != n {
curr.next = head;
head = Some(curr);
}
}
head
}Java
/**
* Time Complexity: O(n)
* Space Complexity: O(n)
*/
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (head != null) {
ListNode curr = head;
stack.push(curr);
head = head.next;
}
int i = 0;
ListNode new_head = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
ListNode node = stack.pop();
++i;
if (i != n) {
node.next = new_head;
new_head = node;
}
}
return new_head;
}Approach 3: Two Pointers
Rust
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
///
/// Space Complexity: O(1)
pub fn remove_nth_from_end(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, n: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut dummy = ListNode::new(-1);
dummy.next = head;
let mut fast = &dummy as *const ListNode;
let mut slow = &mut dummy as *mut ListNode;
unsafe {
for _ in 0..n {
fast = (*fast).next.as_deref().unwrap();
}
loop {
if (*fast).next.is_none() {
break;
}
fast = (*fast).next.as_deref().unwrap();
slow = (*slow).next.as_deref_mut().unwrap();
}
if let Some(mut to_be_del) = (*slow).next.take() {
(*slow).next = to_be_del.next.take();
}
}
dummy.next
}Java
/**
* Time Complexity: O(n)
* Space Complexity: O(1)
*/
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode fast = dummy;
ListNode slow = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}Approach 4: Recursion
Rust
pub fn remove_nth_from_end(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, n: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
const RECURSION_HELPER: fn(Option<Box<ListNode>>, i32) -> (i32, Option<Box<ListNode>>) =
|curr, n| match curr {
None => (0, None),
Some(mut curr) => {
let (level, next) = RECURSION_HELPER(curr.next.take(), n);
curr.next = next;
if level + 1 == n {
(level + 1, curr.next)
} else {
(level + 1, Some(curr))
}
}
};
RECURSION_HELPER(head, n).1
}Java
static class Tuple {
ListNode data;
int level;
}
BiFunction<ListNode, Integer, Tuple> recursionHelper = (curr, n) -> {
if (curr == null) {
return new Tuple(null, 0);
}
Tuple res = this.recursionHelper.apply(curr.next, n);
curr.next = res.data;
return res.level + 1 == n ? new Tuple(curr.next, res.level + 1) : new Tuple(curr, res.level + 1);
};
/**
* Time Complexity: O(n)
* Space Complexity: O(n)
*/
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
return this.recursionHelper.apply(head, n).data;
}