2023/10/23大约 1 分钟
一、题目描述
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即:只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1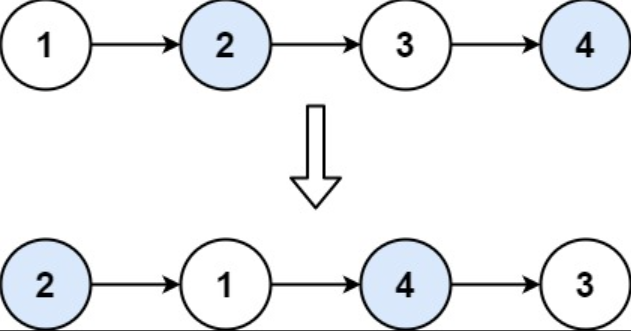
输入: head = [1, 2, 3, 4]
输出: [2, 1, 4, 3]
示例 2
输入: head = []
输出: []
示例 3
输入: head = [1]
输出: [1]
提示
- 链表中节点的数目在范围[0, 100]内
- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
相关主题
- 链表
- 递归
二、题解
ListNode(Rust)
#[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
pub struct ListNode {
pub val: i32,
pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
}
impl ListNode {
#[inline]
fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
ListNode { next: None, val }
}
}ListNode(Java)
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode() {}
public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}方法 1: 迭代
Rust
pub fn swap_pairs(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut dummy = ListNode::new(-1);
dummy.next = head;
let mut p = &mut dummy;
while let Some(mut curr) = p.next.take() {
match curr.next.take() {
None => {
p.next = Some(curr);
break;
}
Some(mut next) => {
curr.next = next.next.take();
next.next = Some(curr);
p.next = Some(next);
p = p.next.as_mut().unwrap().next.as_mut().unwrap();
}
}
}
dummy.next
}Java
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode temp = dummy;
while (temp.next != null) {
ListNode curr = temp.next;
ListNode next = curr.next;
if (next == null) {
break;
}
curr.next = next.next;
next.next = curr;
temp.next = next;
temp = curr;
}
return dummy.next;
}方法 2: 递归
Rust
pub fn swap_pairs(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
const RECURSION_HELPER: fn(Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> =
|curr| match curr {
None => None,
Some(mut curr) => match curr.next.take() {
None => Some(curr),
Some(mut next) => {
curr.next = RECURSION_HELPER(next.next.take());
next.next = Some(curr);
Some(next)
}
},
};
RECURSION_HELPER(head)
}Java
Function<ListNode, ListNode> recursionHelper = (curr) -> {
if (curr == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode next = curr.next;
if (next == null) {
return curr;
}
curr.next = this.recursionHelper.apply(next.next);
next.next = curr;
return next;
};
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
return this.recursionHelper.apply(head);
}