235, 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
大约 4 分钟
一、题目描述
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:"对于有根树T的两个结点p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点x,满足x是p、q的祖先且x的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。"
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, null, null, 3, 5]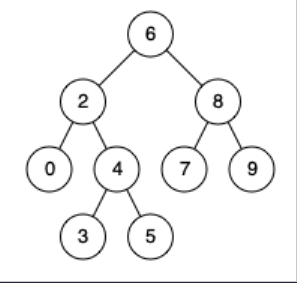
示例 1
输入: root = [6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, null, null, 3, 5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点2和节点8的最近公共祖先是6。
示例 2
输入: root = [6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, null, null, 3, 5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点2和节点4的最近公共祖先是2,因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
提示
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
p、q为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
相关主题
- 树
- 深度优先搜索
- 二叉搜索树
- 二叉树
二、题解
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
}
impl TreeNode {
#[inline]
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
TreeNode {
val,
left: None,
right: None,
}
}
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
方法 1: 两次遍历
pub fn lowest_common_ancestor(
root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
//Self::two_traversal_recur(root, p, q)
Self::two_traversal_iter(root, p, q)
}
fn two_traversal_recur(
root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let p = p.unwrap().borrow().val;
let q = q.unwrap().borrow().val;
const TRAVERSAL: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, i32, &mut Vec<Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>>,) =
|root, target, path| {
if let Some(curr) = root {
let curr_val = curr.borrow().val;
path.push(Some(curr.clone()));
if target > curr_val {
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().right.clone(), target, path);
} else if target < curr_val {
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().left.clone(), target, path);
} else {
return;
}
}
};
let mut p_path = vec![];
TRAVERSAL(root.clone(), p, &mut p_path);
let mut q_path = vec![];
TRAVERSAL(root, q, &mut q_path);
let len = std::cmp::min(p_path.len(), q_path.len());
for i in (0..len).rev() {
if p_path[i] == q_path[i] {
return p_path[i].clone();
}
}
None
}
fn two_traversal_iter(
root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let p = p.unwrap().borrow().val;
let q = q.unwrap().borrow().val;
let traversal = |mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target: i32| {
let mut path = vec![];
while let Some(curr) = root {
let curr_val = curr.borrow().val;
path.push(Some(curr.clone()));
if target > curr_val {
root = curr.borrow().right.clone();
} else if target < curr_val {
root = curr.borrow().left.clone();
} else {
break;
}
}
path
};
let p_path = traversal(root.clone(), p);
let q_path = traversal(root, q);
let len = std::cmp::min(p_path.len(), q_path.len());
for i in (0..len).rev() {
if p_path[i] == q_path[i] {
return p_path[i].clone();
}
}
None
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//return this.twoTraversalRecur(root, p, q);
return this.twoTraversalIter(root, p, q);
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface TriConsumer<A, B, C> {
void accept(A a, B b, C c);
}
TriConsumer<TreeNode, Integer, List<TreeNode>> recur1 = (root, target, path) -> {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
path.add(root);
if (root.val == target) {
return;
}
if (target > root.val) {
this.recur1.accept(root.right, target, path);
} else {
this.recur1.accept(root.left, target, path);
}
};
TreeNode twoTraversalRecur(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
List<TreeNode> pPath = new ArrayList<>();
this.recur1.accept(root, p.val, pPath);
List<TreeNode> qPath = new ArrayList<>();
this.recur1.accept(root, q.val, qPath);
int size = Math.min(pPath.size(), qPath.size());
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (pPath.get(i).val == qPath.get(i).val) {
return pPath.get(i);
}
}
return null;
}
BiFunction<TreeNode, Integer, List<TreeNode>> iter1 = (root, target) -> {
List<TreeNode> path = new ArrayList<>();
while (root != null) {
path.add(root);
if (root.val == target) {
break;
}
if (target > root.val) {
root = root.right;
} else {
root = root.left;
}
}
return path;
};
TreeNode twoTraversalIter(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
List<TreeNode> pPath = this.iter1.apply(root, p.val);
List<TreeNode> qPath = this.iter1.apply(root, q.val);
int size = Math.min(pPath.size(), qPath.size());
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (pPath.get(i).val == qPath.get(i).val) {
return pPath.get(i);
}
}
return null;
}
方法 2: 一次遍历
pub fn lowest_common_ancestor(
root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
//Self::one_traversal_recur(root, p, q
Self::one_traversal_iter(root, p, q)
}
fn one_traversal_recur(
root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let p = p.unwrap().borrow().val;
let q = q.unwrap().borrow().val;
const TRAVERSAL: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, i32, i32) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> =
|root, p, q| match root {
None => None,
Some(curr) => {
let curr_val = curr.borrow().val;
if p < curr_val && q < curr_val {
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().left.clone(), p, q)
} else if p > curr_val && q > curr_val {
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().right.clone(), p, q)
} else {
Some(curr)
}
}
};
TRAVERSAL(root, p, q)
}
fn one_traversal_iter(
root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let p = p.unwrap().borrow().val;
let q = q.unwrap().borrow().val;
let traversal = |mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>| {
while let Some(curr) = root {
let curr_val = curr.borrow().val;
if p < curr_val && q < curr_val {
root = curr.borrow().left.clone();
} else if p > curr_val && q > curr_val {
root = curr.borrow().right.clone();
} else {
return Some(curr);
}
}
None
};
traversal(root)
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//return this.oneTraversalRecur(root, p, q);
return this.oneTraversalIter(root, p, q);
}
BiFunction<TreeNode, int[], TreeNode> recur2 = (root, target) -> {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
int p = target[0];
int q = target[1];
if (p > root.val && q > root.val) {
return this.recur2.apply(root.right, target);
} else if (p < root.val && q < root.val) {
return this.recur2.apply(root.left, target);
} else {
return root;
}
};
TreeNode oneTraversalRecur(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
return this.recur2.apply(root, new int[]{p.val, q.val});
}
BiFunction<TreeNode, int[], TreeNode> iter2 = (root, target) -> {
while (root != null) {
int p = target[0];
int q = target[1];
if (p > root.val && q > root.val) {
root = root.right;
} else if (p < root.val && q < root.val) {
root = root.left;
} else {
break;
}
}
return root;
};
TreeNode oneTraversalIter(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
return this.iter2.apply(root, new int[]{p.val, q.val});
}