2024/1/11大约 3 分钟
一、题目描述
给出二叉搜索树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点node的新值等于原树中大于或等于node.val的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
- 节点的左子树仅包含键小于节点键的节点。
- 节点的右子树仅包含键大于节点键的节点。
- 左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
注意:本题和1038: 从二叉搜索树到更大和树相同
示例 1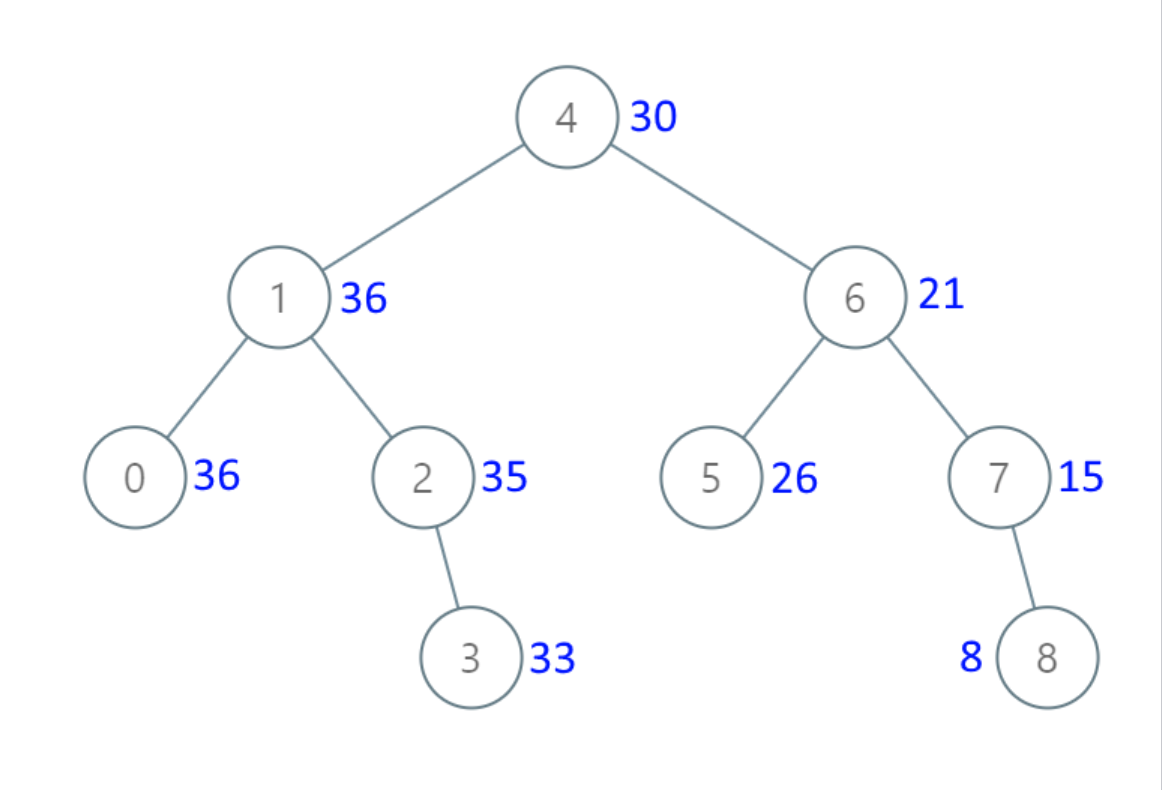
输入: root = [4, 1, 6, 0, 2, 5, 7, null, null, null, 3, null, null, null, 8]
输出: [30, 36, 21, 36, 35, 26, 15, null, null, null, 33, null, null, null, 8]
示例 2
输入: root = [0, null, 1]
输出: [1, null, 1]
示例 3
输入: root = [1, 0, 2]
输出: [3, 3, 2]
示例 4
输入: root = [3, 2, 4, 1]
输出: [7, 9, 4, 10]
提示
- 树中的节点数介于
0和10⁴之间。 - 每个节点的值介于
-10⁴和10⁴之间。 - 树中的所有值互不相同。
- 给定的树为二叉搜索树。
相关主题
- 树
- 深度优先搜索
- 二叉搜索树
- 二叉树
二、题解
Rust节点定义
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
}
impl TreeNode {
#[inline]
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
TreeNode {
val,
left: None,
right: None,
}
}
}Java节点定义
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}方法 1: 镜像中序遍历
Rust
pub fn convert_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
//Self::mirror_in_order_recur_1(root)
//Self::mirror_in_order_iter_1(root)
Self::mirror_in_order_recur_2(root)
}
fn mirror_in_order_recur_1(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let mut sum = 0;
const TRAVERSAL: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, &mut i32) = |root, sum| {
if let Some(curr) = root {
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().right.clone(), sum);
curr.borrow_mut().val += *sum;
*sum = curr.borrow().val;
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().left.clone(), sum);
}
};
TRAVERSAL(root.clone(), &mut sum);
root
}
fn mirror_in_order_iter_1(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if let Some(root) = root.clone() {
let mut sum = 0;
let mut stack = vec![Ok(root)];
while let Some(curr) = stack.pop() {
match curr {
Ok(node) => {
if let Some(left) = node.borrow().left.clone() {
stack.push(Ok(left));
}
stack.push(Err(node.clone()));
if let Some(right) = node.borrow().right.clone() {
stack.push(Ok(right));
}
}
Err(target) => {
target.borrow_mut().val += sum;
sum = target.borrow().val;
}
}
}
}
root
}
fn mirror_in_order_recur_2(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
const TRAVERSAL: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, i32) -> i32 = |root, sum| match root {
None => sum,
Some(curr) => {
let r_sum = TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().right.clone(), sum);
curr.borrow_mut().val += r_sum;
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().left.clone(), curr.borrow().val)
}
};
TRAVERSAL(root.clone(), 0);
root
}Java
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
//return mirrorInorderRecur1(root);
//return mirrorInorderIter1(root);
return mirrorInorderRecur2(root);
}
BiConsumer<TreeNode, int[]> traversal1 = (root, sum) -> {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
this.traversal1.accept(root.right, sum);
root.val += sum[0];
sum[0] = root.val;
this.traversal1.accept(root.left, sum);
};
TreeNode mirrorInorderRecur1(TreeNode root) {
int[] sum = new int[]{0};
this.traversal1.accept(root, sum);
return root;
}
TreeNode mirrorInorderIter1(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
int sum = 0;
Deque<Object[]> stack = new ArrayDeque<>() {{
this.push(new Object[]{false, root});
}};
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Object[] objs = stack.pop();
boolean isTarget = (boolean) objs[0];
TreeNode curr = (TreeNode) objs[1];
if (isTarget) {
curr.val += sum;
sum = curr.val;
} else {
if (curr.left != null) {
stack.push(new Object[]{false, curr.left});
}
stack.push(new Object[]{true, curr});
if (curr.right != null) {
stack.push(new Object[]{false, curr.right});
}
}
}
}
return root;
}
BiFunction<TreeNode, Integer, Integer> traversal2 = (root, sum) -> {
if (root == null) {
return sum;
}
Integer r_sum = this.traversal2.apply(root.right, sum);
root.val += r_sum;
return this.traversal2.apply(root.left, root.val);
};
TreeNode mirrorInorderRecur2(TreeNode root) {
this.traversal2.apply(root, 0);
return root;
}方法 2: Morris镜像中序遍历
Rust
pub fn convert_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let mut root_node = root.clone();
let mut sum = 0;
while let Some(curr) = root_node {
let right = curr.borrow().right.clone();
if right.is_some() {
let mut prev_node = right.clone();
while let Some(ref prev) = prev_node {
let left = prev.borrow().left.clone();
if left.is_none() || left == Some(curr.clone()) {
break;
} else {
prev_node = left;
}
}
match prev_node {
None => break, // this is a mark code
Some(prev) => {
let mut prev = prev.borrow_mut();
if let Some(_) = prev.left.take() {
curr.borrow_mut().val += sum;
sum = curr.borrow().val;
root_node = curr.borrow().left.clone();
} else {
prev.left = Some(curr.clone());
root_node = right;
}
}
}
} else {
curr.borrow_mut().val += sum;
sum = curr.borrow().val;
root_node = curr.borrow().left.clone();
};
}
root
}Java
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode curr = root;
int sum = 0;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.right != null) {
TreeNode prev = curr.right;
while (prev.left != null && prev.left != curr) {
prev = prev.left;
}
if (prev.left == null) {
prev.left = curr;
curr = curr.right;
} else {
prev.left = null;
curr.val += sum;
sum = curr.val;
curr = curr.left;
}
} else {
curr.val += sum;
sum = curr.val;
curr = curr.left;
}
}
return root;
}