1/11/24About 3 min
I Problem
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), convert it to a Greater Tree such that every key of the original BST is changed to the original key plus the sum of all keys greater than the original key in BST.
As a reminder, a binary search tree is a tree that satisfies these constraints:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1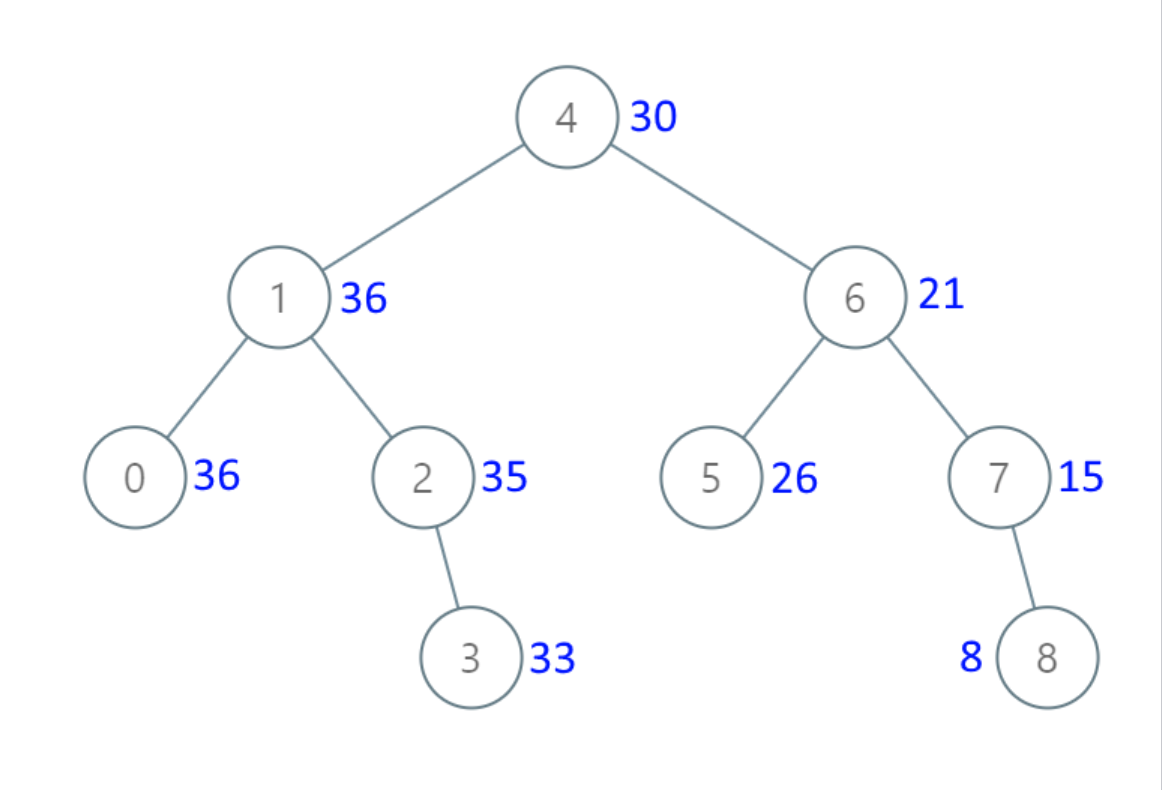
Input: root = [4, 1, 6, 0, 2, 5, 7, null, null, null, 3, null, null, null, 8]
Output: [30, 36, 21, 36, 35, 26, 15, null, null, null, 33, null, null, null, 8]
Example 2
Input: root = [0, null, 1]
Output: [1, null, 1]
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 10⁴]. 10⁴ <= Node.val <= 10⁴- All the values in the tree are unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
NOTE: This question is the same as 1038: Binary Search Tree to Greater Sum Tree.
Related Topics
- Tree
- Depth-First Search
- Binary Search Tree
- Binary Tree
II Solution
Rust Node Definition
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
}
impl TreeNode {
#[inline]
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
TreeNode {
val,
left: None,
right: None,
}
}
}Java Node Definition
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}Approach 1: Mirror In-order Traversal
Rust
pub fn convert_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
//Self::mirror_in_order_recur_1(root)
//Self::mirror_in_order_iter_1(root)
Self::mirror_in_order_recur_2(root)
}
fn mirror_in_order_recur_1(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let mut sum = 0;
const TRAVERSAL: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, &mut i32) = |root, sum| {
if let Some(curr) = root {
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().right.clone(), sum);
curr.borrow_mut().val += *sum;
*sum = curr.borrow().val;
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().left.clone(), sum);
}
};
TRAVERSAL(root.clone(), &mut sum);
root
}
fn mirror_in_order_iter_1(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if let Some(root) = root.clone() {
let mut sum = 0;
let mut stack = vec![Ok(root)];
while let Some(curr) = stack.pop() {
match curr {
Ok(node) => {
if let Some(left) = node.borrow().left.clone() {
stack.push(Ok(left));
}
stack.push(Err(node.clone()));
if let Some(right) = node.borrow().right.clone() {
stack.push(Ok(right));
}
}
Err(target) => {
target.borrow_mut().val += sum;
sum = target.borrow().val;
}
}
}
}
root
}
fn mirror_in_order_recur_2(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
const TRAVERSAL: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, i32) -> i32 = |root, sum| match root {
None => sum,
Some(curr) => {
let r_sum = TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().right.clone(), sum);
curr.borrow_mut().val += r_sum;
TRAVERSAL(curr.borrow().left.clone(), curr.borrow().val)
}
};
TRAVERSAL(root.clone(), 0);
root
}Java
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
//return mirrorInorderRecur1(root);
//return mirrorInorderIter1(root);
return mirrorInorderRecur2(root);
}
BiConsumer<TreeNode, int[]> traversal1 = (root, sum) -> {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
this.traversal1.accept(root.right, sum);
root.val += sum[0];
sum[0] = root.val;
this.traversal1.accept(root.left, sum);
};
TreeNode mirrorInorderRecur1(TreeNode root) {
int[] sum = new int[]{0};
this.traversal1.accept(root, sum);
return root;
}
TreeNode mirrorInorderIter1(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
int sum = 0;
Deque<Object[]> stack = new ArrayDeque<>() {{
this.push(new Object[]{false, root});
}};
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Object[] objs = stack.pop();
boolean isTarget = (boolean) objs[0];
TreeNode curr = (TreeNode) objs[1];
if (isTarget) {
curr.val += sum;
sum = curr.val;
} else {
if (curr.left != null) {
stack.push(new Object[]{false, curr.left});
}
stack.push(new Object[]{true, curr});
if (curr.right != null) {
stack.push(new Object[]{false, curr.right});
}
}
}
}
return root;
}
BiFunction<TreeNode, Integer, Integer> traversal2 = (root, sum) -> {
if (root == null) {
return sum;
}
Integer r_sum = this.traversal2.apply(root.right, sum);
root.val += r_sum;
return this.traversal2.apply(root.left, root.val);
};
TreeNode mirrorInorderRecur2(TreeNode root) {
this.traversal2.apply(root, 0);
return root;
}Approach 2: Morris Mirror In-order Traversal
Rust
pub fn convert_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let mut root_node = root.clone();
let mut sum = 0;
while let Some(curr) = root_node {
let right = curr.borrow().right.clone();
if right.is_some() {
let mut prev_node = right.clone();
while let Some(ref prev) = prev_node {
let left = prev.borrow().left.clone();
if left.is_none() || left == Some(curr.clone()) {
break;
} else {
prev_node = left;
}
}
match prev_node {
None => break, // this is a mark code
Some(prev) => {
let mut prev = prev.borrow_mut();
if let Some(_) = prev.left.take() {
curr.borrow_mut().val += sum;
sum = curr.borrow().val;
root_node = curr.borrow().left.clone();
} else {
prev.left = Some(curr.clone());
root_node = right;
}
}
}
} else {
curr.borrow_mut().val += sum;
sum = curr.borrow().val;
root_node = curr.borrow().left.clone();
};
}
root
}Java
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode curr = root;
int sum = 0;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.right != null) {
TreeNode prev = curr.right;
while (prev.left != null && prev.left != curr) {
prev = prev.left;
}
if (prev.left == null) {
prev.left = curr;
curr = curr.right;
} else {
prev.left = null;
curr.val += sum;
sum = curr.val;
curr = curr.left;
}
} else {
curr.val += sum;
sum = curr.val;
curr = curr.left;
}
}
return root;
}