109, Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
About 2 min
I Problem
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
Example 1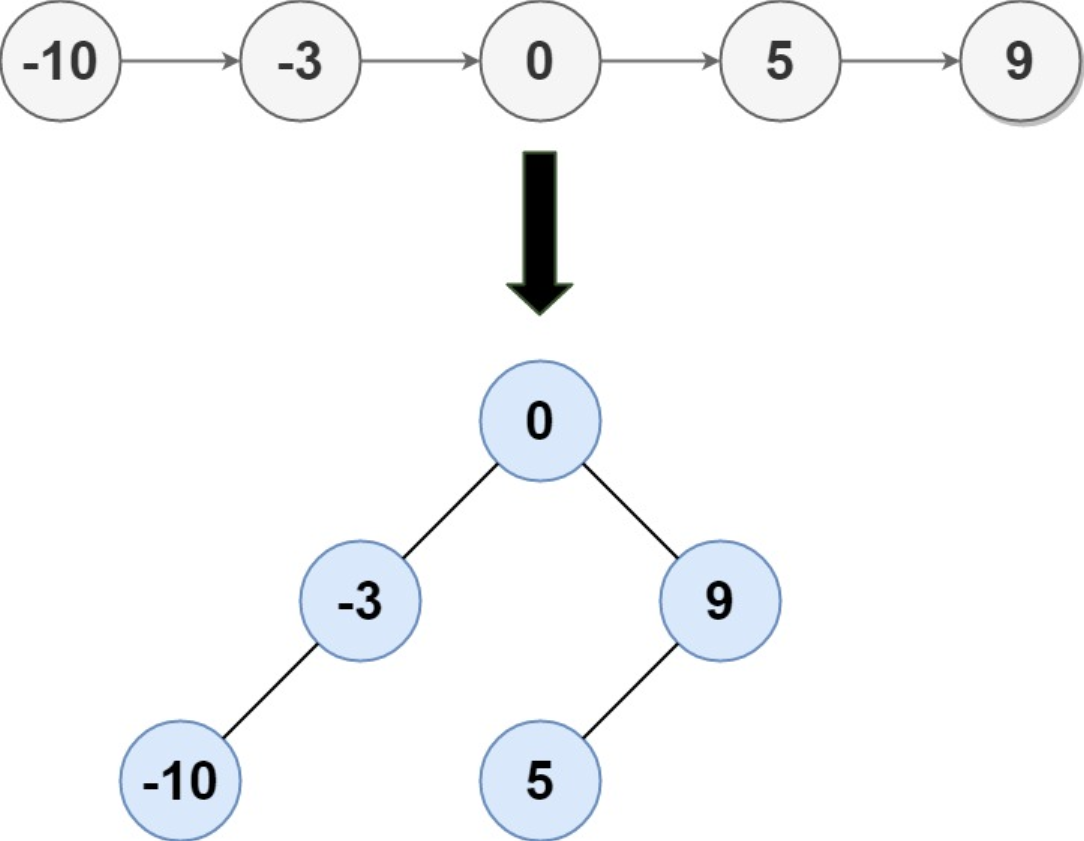
Input: head = [-10, -3, 0, 5, 9]
Output: [0, -3, 9, -10, null, 5]
Explanation: One possible answer is [0, -3, 9, -10, null, 5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints
- The number of nodes in
headis in the range[0, 2 * 10⁴]. -10⁵ <= Node.val <= 10⁵
Related Topics
- Linked List
- Divide and Conquer
- Tree
- Binary Search Tree
- Binary Tree
II Solution
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
}
impl TreeNode {
#[inline]
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
TreeNode {
val,
left: None,
right: None,
}
}
}
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct ListNode {
pub val: i32,
pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
}
impl ListNode {
#[inline]
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
ListNode {
val,
next: None
}
}
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode() {}
public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
Approach 1: Divide and Conquer
///
/// Time Complexity: O(nlog(n))
/// Space Complexity: O(log(n))
///
pub fn sorted_list_to_bst(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
const GET_MID: for<'a> fn(Option<&'a Box<ListNode>>, Option<&'a Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<&'a Box<ListNode>> =
|left, right| {
let mut slow = left;
let mut fast = left;
while fast != right && fast.is_some_and(|fast| fast.next.as_ref() != right) {
fast.map(|f| {
fast = f.next.as_ref();
});
fast.map(|f| {
fast = f.next.as_ref();
});
slow.map(|s| {
slow = s.next.as_ref();
});
}
slow
};
const CONVERT: fn(Option<&Box<ListNode>>, Option<&Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> =
|left, right| {
if left == right {
return None;
}
let mid = GET_MID(left, right);
let mut root = if let Some(mid) = mid {
Some(Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode::new(mid.val))))
} else {
None
};
root.as_mut().map(|curr| {
curr.borrow_mut().left = CONVERT(left, mid);
curr.borrow_mut().right = CONVERT(mid.and_then(|mid| mid.next.as_ref()), right);
});
root
};
CONVERT(head.as_ref(), None)
}
BiFunction<ListNode, ListNode, ListNode> getMid = (left, right) -> {
ListNode slow = left;
ListNode fast = left;
while (fast != right && fast.next != right) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
};
BiFunction<ListNode, ListNode, TreeNode> convert1 = (left, right) -> {
if (left == right) {
return null;
}
ListNode mid = this.getMid.apply(left, right);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(mid.val);
root.left = this.convert1.apply(left, mid);
root.right = this.convert1.apply(mid.next, right);
return root;
};
/**
* Time Complexity:O(nlog(n))
* Space Complexity:O(log(n))
*/
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
return this.convert1.apply(head, null);
}
Approach 2: Divide and Conquer with In-order Traversal
///
/// Time Complexity: O(n)
/// Space Complexity: O(log(n))
///
pub fn sorted_list_to_bst(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let get_len = |mut curr: Option<&Box<ListNode>>| {
let mut len = 0;
while let Some(c) = curr {
len += 1;
curr = c.next.as_ref();
}
len
};
let len = get_len(head.as_ref());
const CONVERT: fn(&mut Option<Box<ListNode>>, usize, usize) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> =
|head, left, right| {
if left == right {
return None;
}
let mid = (left + right) / 2;
let root = Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode::new(0)));
root.borrow_mut().left = CONVERT(head, left, mid);
root.borrow_mut().val = head.take().map_or(0, |mut h| {
let val = h.val;
*head = h.next.take();
val
});
root.borrow_mut().right = CONVERT(head, mid + 1, right);
Some(root)
};
CONVERT(&mut head, 0, len)
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface TriFunction<A, B, C, D> {
D apply(A a, B b, C c);
}
Function<ListNode, Integer> getSize = (head) -> {
int size = 0;
while (head != null){
size++;
head = head.next;
}
return size;
};
TriFunction<ListNode[], Integer, Integer, TreeNode> convert2 = (head, left, right) -> {
if (Objects.equals(left, right)) {
return null;
}
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(0);
root.left = this.convert2.apply(head, left, mid);
root.val = head[0].val;
head[0] = head[0].next;
root.right = this.convert2.apply(head, mid + 1, right);
return root;
};
/**
* Time Complexity:O(n)
* Space Complexity:O(log(n))
*/
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
int size = this.getSize.apply(head);
return this.convert2.apply(new ListNode[]{head}, 0, size);
}