1/10/24About 5 min
I Problem
Given the root of a binary search tree (BST) with duplicates, return all the mode(s) (i.e., the most frequently occurred element) in it.
If the tree has more than one mode, return them in any order.
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than or equal to the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1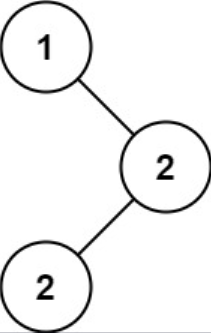
Input: root = [1, null, 2, 2]
Output: [2]
Example 2
Input: root = [0]
Output: [0]
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10⁴]. -10⁵ <= Node.val <= 10⁵
Follow up
Could you do that without using any extra space? (Assume that the implicit stack space incurred due to recursion does not count).
Related Topics
- Tree
- Depth-First Search
- Binary Search Tree
- Binary Tree
II Solution
Rust Node Definition
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
}
impl TreeNode {
#[inline]
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
TreeNode {
val,
left: None,
right: None,
}
}
}
/// val: The value of the node being traversed
/// curr_val: Value being processed
/// curr_freq: The frequency of occurrences of values being processed
/// max_freq: Maximum frequency of occurrence
/// res: result
fn update(val: i32, curr_val: &mut i32, curr_freq: &mut usize, max_freq: &mut usize, res: &mut Vec<i32>) {
if val == *curr_val {
*curr_freq += 1;
} else {
*curr_val = val;
*curr_freq = 1;
}
if *curr_freq > *max_freq {
res.clear();
*max_freq = *curr_freq;
}
if *curr_freq == *max_freq {
res.push(val);
}
}Java Node Definition
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
/**
* val: The value of the node being traversed
* params:
* 0: Value being processed
* 1: The frequency of occurrences of values being processed
* 2: Maximum frequency of occurrence
* res: result
*/
TriConsumer<Integer, int[], List<Integer>> update = (val, params, res) -> {
if (val == params[0]) {
params[1]++;
} else {
params[0] = val;
params[1] = 1;
}
if (params[1] > params[2]) {
res.clear();
params[2] = params[1];
}
if (params[1] == params[2]) {
res.add(val);
}
};Approach 1: Count Frequency With Hash Map
Rust
pub fn find_mode(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
//Self::use_hashmap_recur(root)
Self::use_hashmap_iter(root)
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n)
/// Space complexity: O(n)
///
fn use_hashmap_recur(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut map = HashMap::new();
const PREORDER: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, &mut HashMap<i32, usize>) =
|root, counter| {
if let Some(curr) = root {
let curr_val = curr.borrow().val;
counter
.entry(curr_val)
.and_modify(|count| *count += 1)
.or_insert(1);
PREORDER(curr.borrow_mut().left.take(), counter);
PREORDER(curr.borrow_mut().right.take(), counter);
}
};
PREORDER(root, &mut map);
let max_freq = map.values().max().map(|v| *v).unwrap_or_default();
map.into_iter()
.filter_map(|(k, v)| {
if v == max_freq {
return Some(k);
}
None
})
.collect()
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n)
/// Space complexity: O(n)
///
fn use_hashmap_iter(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut map = HashMap::new();
if let Some(root) = root {
let mut stack = vec![root];
while let Some(curr) = stack.pop() {
let curr_val = curr.borrow().val;
map.entry(curr_val)
.and_modify(|count| *count += 1)
.or_insert(1);
if let Some(right) = curr.borrow_mut().right.take() {
stack.push(right);
}
if let Some(left) = curr.borrow_mut().left.take() {
stack.push(left);
}
}
}
let max_freq = map.values().max().map(|v| *v).unwrap_or_default();
map.into_iter()
.filter_map(|(k, v)| {
if v == max_freq {
return Some(k);
}
None
})
.collect()
}Java
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
//return this.useHashmapRecur(root);
return this.useHashmapIter(root);
}
BiConsumer<TreeNode, Map<Integer, Integer>> preorder = (root, counter) -> {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
counter.put(root.val, counter.getOrDefault(root.val, 0) + 1);
this.preorder.accept(root.left, counter);
this.preorder.accept(root.right, counter);
};
/**
* Time complexity: O(n)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*/
int[] useHashmapRecur(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, Integer> counter = new HashMap<>();
this.preorder.accept(root, counter);
Integer maxFreq = counter.values().stream().max(Comparator.naturalOrder()).orElse(0);
return counter.entrySet().stream()
.filter(e -> Objects.equals(e.getValue(), maxFreq))
.map(Map.Entry::getKey).mapToInt(Integer::intValue)
.toArray();
}
/**
* Time complexity: O(n)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*/
int[] useHashmapIter(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, Integer> counter = new HashMap<>();
if (root != null) {
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>() {{
this.push(root);
}};
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode curr = stack.pop();
counter.put(curr.val, counter.getOrDefault(curr.val, 0) + 1);
if (curr.right != null) {
stack.push(curr.right);
}
if (curr.left != null) {
stack.push(curr.left);
}
}
}
Integer maxFreq = counter.values().stream().max(Comparator.naturalOrder()).orElse(0);
return counter.entrySet().stream()
.filter(e -> Objects.equals(e.getValue(), maxFreq))
.map(Map.Entry::getKey).mapToInt(Integer::intValue)
.toArray();
}Approach 2: In-order Traversal
Rust
pub fn find_mode(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
//Self::in_order_traversal_recur(root)
Self::in_order_traversal_iter(root)
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n)
/// Space complexity: O(n)
///
fn in_order_traversal_recur(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut res = vec![];
let mut curr_val = i32::MIN;
let mut curr_freq = 0;
let mut max_freq = 0;
const INORDER: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, &mut i32, &mut usize, &mut usize, &mut Vec<i32>) =
|root, curr_val, curr_freq, max_freq, res| {
if let Some(curr) = root {
INORDER(curr.borrow_mut().left.take(), curr_val, curr_freq, max_freq, res);
let val = curr.borrow().val;
Solution::update(val, curr_val, curr_freq, max_freq, res);
INORDER(curr.borrow_mut().right.take(), curr_val, curr_freq, max_freq, res);
}
};
INORDER(root, &mut curr_val, &mut curr_freq, &mut max_freq, &mut res);
res
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n)
/// Space complexity: O(n)
///
fn in_order_traversal_iter(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut res = vec![];
if let Some(root) = root {
let mut curr_val = i32::MIN;
let mut curr_freq = 0;
let mut max_freq = 0;
let mut stack = vec![Ok(root)];
while let Some(curr) = stack.pop() {
match curr {
Ok(node) => {
if let Some(right) = node.borrow_mut().right.take() {
stack.push(Ok(right));
}
stack.push(Err(node.borrow().val));
if let Some(left) = node.borrow_mut().left.take() {
stack.push(Ok(left));
}
}
Err(val) => {
Solution::update(val, &mut curr_val, &mut curr_freq, &mut max_freq, &mut res);
}
}
}
}
res
}Java
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
//return this.inorderTraversalRecur(root);
return this.inorderTraversalIter(root);
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface TriConsumer<A, B, C> {
void accept(A a, B b, C c);
}
TriConsumer<TreeNode, int[], List<Integer>> inorder = (root, params, res) -> {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
this.inorder.accept(root.left, params, res);
this.update.accept(root.val, params, res);
this.inorder.accept(root.right, params, res);
};
/**
* Time complexity: O(n)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*/
int[] inorderTraversalRecur(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] params = {Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0, 0};
this.inorder.accept(root, params, res);
return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
/**
* Time complexity: O(n)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*/
int[] inorderTraversalIter(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
int[] params = new int[]{Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0, 0};
Deque<Object> stack = new ArrayDeque<>() {{
this.push(root);
}};
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Object obj = stack.pop();
switch (obj) {
case TreeNode curr -> {
if (curr.right != null) {
stack.push(curr.right);
}
stack.push(curr.val);
if (curr.left != null) {
stack.push(curr.left);
}
}
case Integer val -> {
this.update.accept(val, params, res);
}
default -> throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected value: " + obj);
}
}
}
return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}Approach 3: Morris In-order Traversal
Rust
pub fn find_mode(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
//Self::morris_in_order_iter_1(root)
Self::morris_in_order_iter_2(root)
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n)
/// Space complexity: O(1)
///
fn morris_in_order_iter_1(mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut res = vec![];
let mut curr_val = i32::MIN;
let mut curr_freq = 0;
let mut max_freq = 0;
while let Some(curr) = root {
let val = curr.borrow().val;
let left = curr.borrow().left.clone();
if left.is_some() {
let mut prev_node = left.clone();
while let Some(ref prev) = prev_node {
let right = prev.borrow().right.clone();
if right.is_none() || right == Some(curr.clone()) {
break;
} else {
prev_node = right;
}
}
match prev_node {
None => break, // this is mark code
Some(prev) => {
let mut prev = prev.borrow_mut();
if let Some(_) = prev.right.take() {
Solution::update(val, &mut curr_val, &mut curr_freq, &mut max_freq, &mut res);
root = curr.borrow().right.clone();
} else {
prev.right = Some(curr);
root = left;
}
}
}
} else {
Solution::update(val, &mut curr_val, &mut curr_freq, &mut max_freq, &mut res);
root = curr.borrow().right.clone();
};
}
res
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n)
/// Space complexity: O(1)
///
fn morris_in_order_iter_2(mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut res = vec![];
let mut curr_val = i32::MIN;
let mut curr_freq = 0;
let mut max_freq = 0;
while let Some(curr) = root {
let left = curr.borrow().left.clone();
let val = curr.borrow().val;
if left.is_none() {
Solution::update(val, &mut curr_val, &mut curr_freq, &mut max_freq, &mut res);
root = curr.borrow().right.clone();
continue;
}
let mut prev_node = left.clone();
while let Some(ref prev) = prev_node {
let right = prev.borrow().right.clone();
if right.is_none() || right == Some(curr.clone()) {
break;
} else {
prev_node = right;
}
}
if let Some(prev) = prev_node {
let mut prev = prev.borrow_mut();
if let Some(_) = prev.right.take() {
Solution::update(val, &mut curr_val, &mut curr_freq, &mut max_freq, &mut res);
root = curr.borrow().right.clone();
} else {
prev.right = Some(curr);
root = left;
}
} else {
// here is mark code
//root = None;
break;
}
}
res
}Java
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
//return this.morrisInorderIter1(root);
return this.morrisInorderIter2(root);
}
/**
* Time complexity: O(n)
* Space complexity: O(1)
*/
int[] morrisInorderIter1(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] params = new int[]{Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0, 0};
TreeNode prev = null;
while (root != null) {
if (root.left != null) {
prev = root.left;
while (prev.right != null && prev.right != root) {
prev = prev.right;
}
if (prev.right == null) {
prev.right = root;
root = root.left;
} else {
prev.right = null;
this.update.accept(root.val, params, res);
root = root.right;
}
} else {
this.update.accept(root.val, params, res);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
/**
* Time complexity: O(n)
* Space complexity: O(1)
*/
int[] morrisInorderIter2(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] params = new int[]{Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0, 0};
TreeNode prev = null;
while (root != null) {
if (root.left == null) {
this.update.accept(root.val, params, res);
root = root.right;
continue;
}
prev = root.left;
while (prev.right != null && prev.right != root) {
prev = prev.right;
}
if (prev.right == null) {
prev.right = root;
root = root.left;
} else {
prev.right = null;
this.update.accept(root.val, params, res);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}