1/18/24About 2 min
I Problem
Given the root of a binary search tree and the lowest and highest boundaries as low and high, trim the tree so that all its elements lies in [low, high]. Trimming the tree should not change the relative structure of the elements that will remain in the tree (i.e., any node's descendant should remain a descendant). It can be proven that there is a unique answer.
Return the root of the trimmed binary search tree. Note that the root may change depending on the given bounds.
Example 1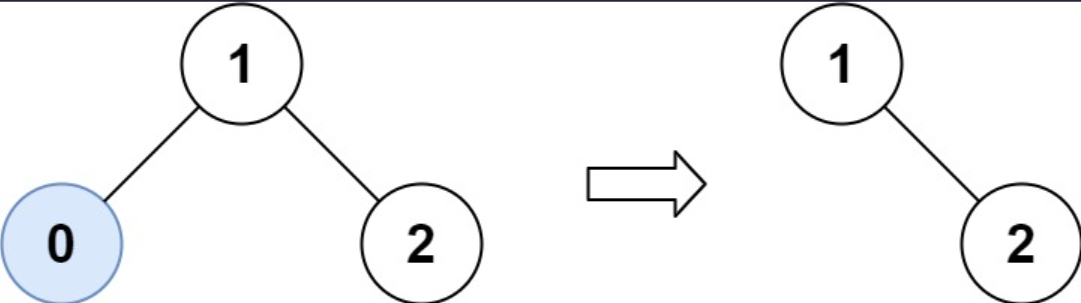
Input: root = [1, 0, 2], low = 1, high = 2
Output: [1, null, 2]
Example 2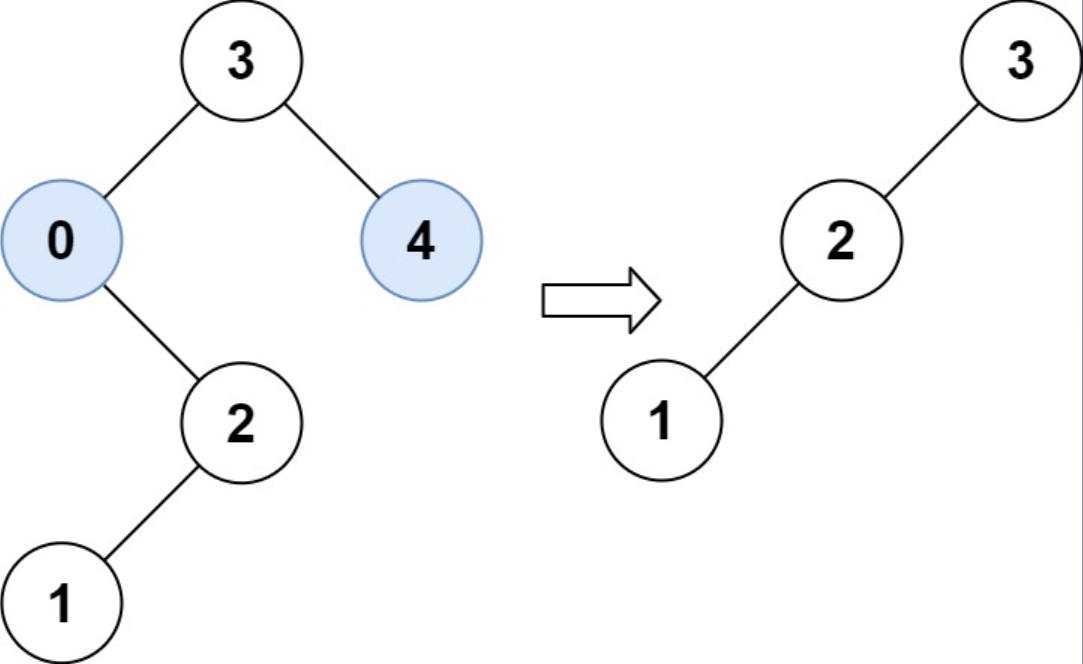
Input: root = [3, 0, 4, null, 2, null, null, 1], low = 1, high = 3
Output: [3, 2, null, 1]
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10⁴]. 0 <= Node.val <= 10⁴- The value of each node in the tree is unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.0 <= low <= high <= 10⁴
Related Topics
- Tree
- Binary Tree
- Binary Search Tree
- Depth-First Search
II Solution
Rust Node Definition
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
}
impl TreeNode {
#[inline]
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
TreeNode {
val,
left: None,
right: None,
}
}
}Java Node Definition
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}Approach 1: Recursion
Rust
pub fn trim_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, low: i32, high: i32) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
const TRIM: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, i32, i32) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> =
|root, low, high| match root {
None => None,
Some(curr) => {
let curr_val = curr.borrow().val;
if curr_val < low {
TRIM(curr.borrow_mut().right.take(), low, high)
} else if curr_val > high {
TRIM(curr.borrow_mut().left.take(), low, high)
} else {
let left = curr.borrow_mut().left.take();
let right = curr.borrow_mut().right.take();
curr.borrow_mut().left = TRIM(left, low, high);
curr.borrow_mut().right = TRIM(right, low, high);
Some(curr)
}
}
};
TRIM(root, low, high)
}Java
@FunctionalInterface
interface TriFunction<A, B, C, D> {
D apply(A a, B b, C c);
}
TriFunction<TreeNode, Integer, Integer, TreeNode> recur = (root, low, high) -> {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val < low) {
return this.recur.apply(root.right, low, high);
} else if (root.val > high) {
return this.recur.apply(root.left, low, high);
} else {
root.left = this.recur.apply(root.left, low, high);
root.right = this.recur.apply(root.right, low, high);
return root;
}
};
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
return this.recur.apply(root, low, high);
}Approach 2: Iteration
Rust
pub fn trim_bst(mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, low: i32, high: i32) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
while let Some(curr) = root {
let curr_val = curr.borrow().val;
if curr_val < low {
root = curr.borrow_mut().right.take();
} else if curr_val > high {
root = curr.borrow_mut().left.take();
} else {
root = Some(curr);
break;
}
}
if root.is_none() {
return None;
}
let mut left_node = root.clone();
while let Some(ref curr) = left_node {
let left = curr.borrow().left.clone();
if let Some(left) = left {
if left.borrow().val < low {
curr.borrow_mut().left = left.borrow_mut().right.take();
} else {
left_node = Some(left);
}
} else {
break;
};
}
let mut right_node = root.clone();
while let Some(ref curr) = right_node {
let right = curr.borrow().right.clone();
if let Some(right) = right {
if right.borrow().val > high {
curr.borrow_mut().right = right.borrow_mut().left.take();
} else {
right_node = Some(right);
}
} else {
break;
};
}
root
}Java
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
while (root != null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)) {
if (root.val < low) {
root = root.right;
} else {
root = root.left;
}
}
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
for (TreeNode curr = root; curr.left != null;) {
TreeNode left = curr.left;
if (left.val < low) {
curr.left = left.right;
} else {
curr = left;
}
}
for (TreeNode curr = root; curr.right != null;) {
TreeNode right = curr.right;
if (right.val > high) {
curr.right = right.left;
} else {
curr = right;
}
}
return root;
}