1/4/24About 4 min
I Problem
You are given an integer array nums with no duplicates. A maximum binary tree can be built recursively from nums using the following algorithm:
- Create a root node whose value is the maximum value in
nums. - Recursively build the left subtree on the subarray prefix to the left of the maximum value.
- Recursively build the right subtree on the subarray suffix to the right of the maximum value.
Return the maximum binary tree built from nums.
Example 1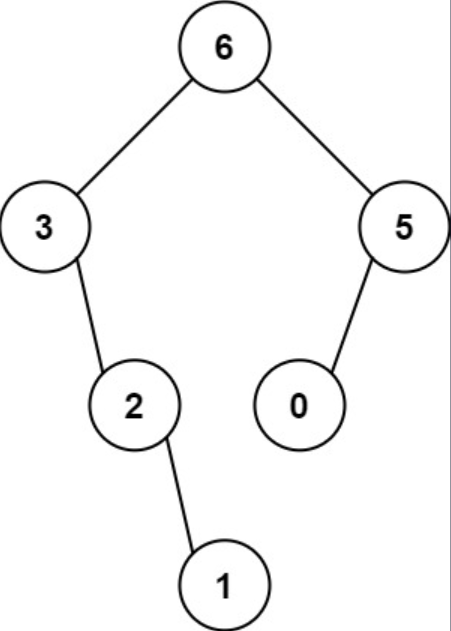
Input: nums = [3, 2, 1, 6, 0, 5]
Output: [6, 3, 5, null, 2, 0, null, null, 1]
Explanation: The recursive calls are as follow:
- The largest value in [3, 2, 1, 6, 0, 5] is 6. Left prefix is [3, 2, 1] and right suffix is [0, 5].
- The largest value in [3, 2, 1] is 3. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [2, 1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- The largest value in [2, 1] is 2. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 1.
- The largest value in [0, 5] is 5. Left prefix is [0] and right suffix is [].
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 0.
- Empty array, so no child.Example 2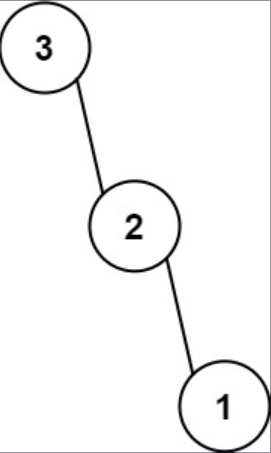
Input: nums = [3, 2, 1]
Output: [3, null, 2, null, 1]
Constraints
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 1000- All integers in
numsare unique
Related Topics
- Array
- Divide and Conquer
- Stack
- Tree
- Monotonic Stack
- Binary Tree
II Solution
Rust Node Definition
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
}
impl TreeNode {
#[inline]
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
TreeNode {
val,
left: None,
right: None,
}
}
}Java Node Definition
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}Approach 1: Recursion
Rust
pub fn construct_maximum_binary_tree(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
//Self::recur_1(nums)
Self::recur_2(nums)
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n^2)
/// Space complexity: O(n)
///
fn recur_1(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
const RECUR: fn(&[i32]) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> = |nums| {
let len = nums.len();
if len == 0 {
return None;
}
let (max_idx, max_val) = nums
.iter()
.enumerate()
.max_by(|&(_, a), &(_, b)| a.cmp(b))
.map(|(idx, &val)| (idx, val))
.unwrap_or_default();
let root = Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode::new(max_val)));
if len == 1 {
return Some(root);
}
let (left_nums, right_nums) = (&nums[..max_idx], &nums[max_idx + 1..]);
root.borrow_mut().left = RECUR(left_nums);
root.borrow_mut().right = RECUR(right_nums);
Some(root)
};
RECUR(&nums)
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n^2)
/// Space complexity: O(n)
///
fn recur_2(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
const RECUR: fn(&[i32], usize, usize) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> =
|nums, l_idx, r_idx| {
let len = r_idx - l_idx;
if len == 0 {
return None;
}
let (max_idx, max_val) = nums[l_idx..r_idx]
.iter()
.enumerate()
.max_by(|&(_, a), &(_, b)| a.cmp(b))
.map(|(idx, val)| (idx + l_idx, *val))
.unwrap_or_default();
let root = Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode::new(max_val)));
if len == 1 {
return Some(root);
}
root.borrow_mut().left = RECUR(nums, l_idx, max_idx);
root.borrow_mut().right = RECUR(nums, max_idx + 1, r_idx);
Some(root)
};
RECUR(&nums, 0, nums.len())
}Java
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
//return this.recur1(nums);
return this.recur2(nums);
}
Function<List<Integer>, int[]> getMaxAndIdx = nums -> {
int[] res = new int[]{Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0};
for (int i = 0, size = nums.size(); i < size; i++) {
if (nums.get(i) > res[0]) {
res[0] = nums.get(i);
res[1] = i;
}
}
return res;
};
Function<List<Integer>, TreeNode> helper1 = nums -> {
int size = nums.size();
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int[] valAndIdx = this.getMaxAndIdx.apply(nums);
int maxVal = valAndIdx[0];
int maxIdx = valAndIdx[1];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxVal);
if (size == 1) {
return root;
}
root.left = this.helper1.apply(nums.subList(0, maxIdx));
root.right = this.helper1.apply(nums.subList(maxIdx + 1, size));
return root;
};
/**
* Time complexity: O(n^2)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*/
TreeNode recur1(int[] _nums) {
List<Integer> nums = Arrays.stream(_nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
return this.helper1.apply(nums);
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface TriFunction<A, B, C, D> {
D apply(A a, B b, C c);
}
TriFunction<List<Integer>, Integer, Integer, TreeNode> helper2 = (nums, lIdx, rIdx) -> {
int size = rIdx - lIdx;
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int[] valAndIdx = this.getMaxAndIdx.apply(nums.subList(lIdx, rIdx));
int maxVal = valAndIdx[0];
int maxIdx = valAndIdx[1] + lIdx;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxVal);
if (size == 1) {
return root;
}
root.left = this.helper2.apply(nums, lIdx, maxIdx);
root.right = this.helper2.apply(nums, maxIdx + 1, rIdx);
return root;
};
/**
* Time complexity: O(n^2)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*/
TreeNode recur2(int[] _nums) {
List<Integer> nums = Arrays.stream(_nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
return this.helper2.apply(nums, 0, _nums.length);
}Approach 2: Monotonic Stack
Rust
pub fn construct_maximum_binary_tree(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
//Self::monotonic_stack_1(nums)
Self::monotonic_stack_2(nums)
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n)
/// Space complexity: O(n)
///
fn monotonic_stack_1(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let len = nums.len();
if len == 0 {
return None;
}
let mut stack = Vec::with_capacity(len);
let mut left = vec![usize::MAX; len];
let mut right = vec![usize::MAX; len];
let mut tree = Vec::with_capacity(len);
for i in 0..len {
tree.push(Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode::new(nums[i]))));
while let Some(&last) = stack.last() {
if !(nums[i] > nums[last]) {
break;
}
right[last] = i;
stack.pop();
}
if let Some(&last) = stack.last() {
left[i] = last;
}
stack.push(i);
}
let mut root = None;
for i in 0..len {
if left[i] == usize::MAX && right[i] == usize::MAX {
root = Some(tree[i].clone());
} else if right[i] == usize::MAX
|| (left[i] != usize::MAX && nums[left[i]] < nums[right[i]])
{
tree[left[i]].borrow_mut().right = Some(tree[i].clone());
} else {
tree[right[i]].borrow_mut().left = Some(tree[i].clone());
}
}
root
}
///
/// Time complexity: O(n)
/// Space complexity: O(n)
///
fn monotonic_stack_2(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let len = nums.len();
if len == 0 {
return None;
}
let mut stack: Vec<usize> = Vec::with_capacity(len);
let mut tree = Vec::with_capacity(len);
for i in 0..len {
tree.push(Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode::new(nums[i]))));
while let Some(&last) = stack.last() {
if !(nums[i] > nums[last]) {
break;
}
tree[i].borrow_mut().left = Some(tree[last].clone());
stack.pop();
}
if let Some(&last) = stack.last() {
tree[last].borrow_mut().right = Some(tree[i].clone())
}
stack.push(i);
}
Some(tree[stack[0]].clone())
}Java
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
//return this.monotonicStack1(nums);
return this.monotonicStack2(nums);
}
/**
* Time complexity: O(n)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*/
TreeNode monotonicStack1(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if (len == 0) {
return null;
}
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>(len);
TreeNode[] tree = new TreeNode[len];
int[] left = new int[len];
int[] right = new int[len];
Arrays.fill(left, -1);
Arrays.fill(right, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
tree[i] = new TreeNode(nums[i]);
while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i] > nums[stack.peek()]) {
right[stack.pop()] = i;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
left[i] = stack.peek();
}
stack.push(i);
}
TreeNode root = null;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (left[i] == -1 && right[i] == -1) {
root = tree[i];
} else if (right[i] == -1 || (left[i] != -1 && nums[left[i]] < nums[right[i]])) {
tree[left[i]].right = tree[i];
} else {
tree[right[i]].left = tree[i];
}
}
return root;
}
/**
* Time complexity: O(n)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*/
TreeNode monotonicStack2(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if (len == 0) {
return null;
}
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>(len);
TreeNode[] tree = new TreeNode[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
tree[i] = new TreeNode(nums[i]);
while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i] > nums[stack.peek()]) {
tree[i].left = tree[stack.pop()];
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
tree[stack.peek()].right = tree[i];
}
stack.push(i);
}
// Here we should get the element at the bottom of the stack
return tree[stack.getLast()];
}