12/29/23About 5 min
I Problem
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer target_sum, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals target_sum.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1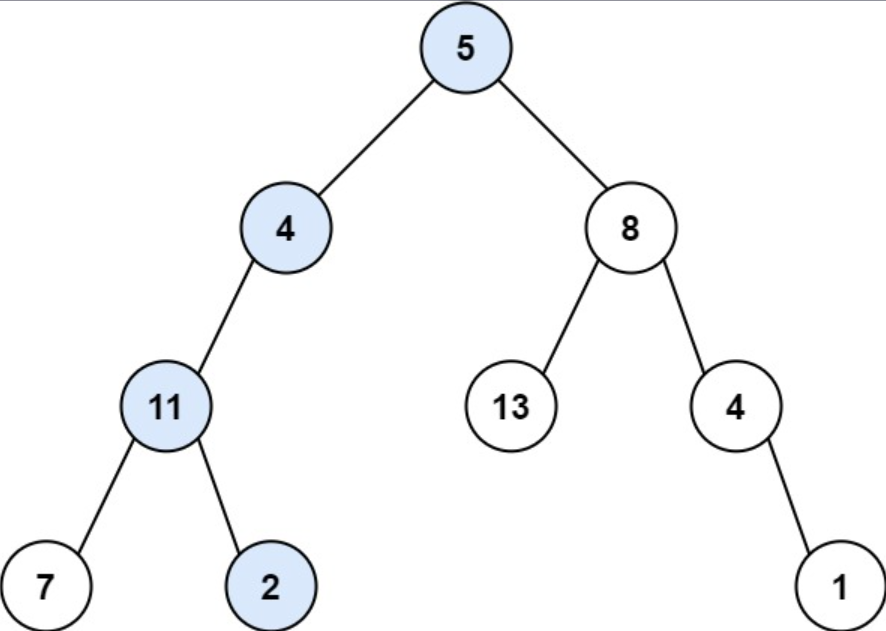
Input: root = [5, 4, 8, 11, null, 13, 4, 7, 2, null, null, null, 1], targetSum = 22
Output: true
Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.
Example 2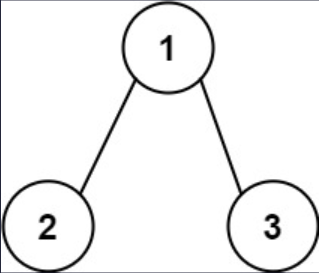
Input: root = [1, 2, 3], targetSum = 5
Output: false
Explanation: There two root-to-leaf paths in the tree:
(1 --> 2): The sum is 3.
(1 --> 3): The sum is 4.
There is no root-to-leaf path with sum = 5.
Example 3
Input: root = [], targetSum = 0
Output: false
Explanation: Since the tree is empty, there are no root-to-leaf paths.
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Related Topics
- Tree
- Depth-First Search
- Breadth-First Search
- Binary Tree
II Solution
Rust Node Definition
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
}
impl TreeNode {
#[inline]
pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
TreeNode {
val,
left: None,
right: None,
}
}
}Java Node Definition
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}Approach 1: Depth-First Search
Rust
pub fn has_path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
//Self::dfs_recur_1(root, target_sum)
//Self::dfs_iter_1(root, target_sum)
//Self::dfs_recur_2(root, target_sum)
Self::dfs_iter_2(root, target_sum)
}
///
/// 1. Find all the paths
/// 2. Compare the sum of one path with target_sum
///
fn dfs_recur_1(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
let mut paths = vec![];
const RECUR: fn(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, Vec<i32>, &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) =
|root, mut path, paths| {
if let Some(curr) = root {
path.push(curr.borrow().val);
let left = curr.borrow_mut().left.take();
let right = curr.borrow_mut().right.take();
if left.is_none() && right.is_none() {
paths.push(path);
} else {
if left.is_some() {
RECUR(left, path.clone(), paths);
}
if right.is_some() {
RECUR(right, path, paths);
}
}
}
};
RECUR(root, vec![], &mut paths);
paths
.into_iter()
.any(|p| p.into_iter().sum::<i32>() == target_sum)
}
fn dfs_iter_1(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
let mut paths = vec![];
if let Some(root) = root {
let mut stack = vec![(root, vec![])];
while let Some((curr, mut path)) = stack.pop() {
path.push(curr.borrow().val);
let left = curr.borrow_mut().left.take();
let right = curr.borrow_mut().right.take();
if left.is_none() && right.is_none() {
paths.push(path);
} else {
if let Some(right) = right {
stack.push((right, path.clone()));
}
if let Some(left) = left {
stack.push((left, path));
}
}
}
}
paths
.into_iter()
.any(|p| p.into_iter().sum::<i32>() == target_sum)
}
///
/// Accumulate val on each path and compare when reaching the leaf node
///
fn dfs_recur_2(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
const RECUR: fn(Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, i32, i32) -> bool =
|root, sum, target_sum| match root {
None => false,
Some(curr) => {
let curr_sum = curr.borrow().val + sum;
let left = curr.borrow_mut().left.take();
let right = curr.borrow_mut().right.take();
match (left, right) {
(None, None) => curr_sum == target_sum,
(None, right) => RECUR(right, curr_sum, target_sum),
(left, None) => RECUR(left, curr_sum, target_sum),
(left, right) => {
RECUR(left, curr_sum, target_sum) || RECUR(right, curr_sum, target_sum)
}
}
}
};
RECUR(root, 0, target_sum)
}
fn dfs_iter_2(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
if let Some(root) = root {
let mut stack = vec![(root, 0)];
while let Some((curr, sum)) = stack.pop() {
let curr_sum = curr.borrow().val + sum;
let left = curr.borrow_mut().left.take();
let right = curr.borrow_mut().right.take();
if left.is_none() && right.is_none() && curr_sum == target_sum {
return true;
}
if let Some(right) = right {
stack.push((right, curr_sum));
}
if let Some(left) = left {
stack.push((left, curr_sum));
}
}
}
false
}Java
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
//return this.dfsRecur1(root, targetSum);
//return this.dfsIter1(root, targetSum);
//return this.dfsRecur2(root, targetSum);
return this.dfsIter2(root, targetSum);
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface TriConsumer<A, B, C> {
void accept(A a, B b, C c);
}
TriConsumer<TreeNode, List<Integer>, List<List<Integer>>> recur1 = (root, path, paths) -> {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
path.add(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
paths.add(path);
} else {
if (root.left != null) {
this.recur1.accept(root.left, new ArrayList<>(path), paths);
}
if (root.right != null) {
this.recur1.accept(root.right, path, paths);
}
}
};
/**
* 1. Find all the paths
* 2. Compare the sum of one path with target_sum
*/
boolean dfsRecur1(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>();
this.recur1.accept(root, new ArrayList<>(), paths);
return paths.stream().anyMatch(p ->
p.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum() == targetSum
);
}
boolean dfsIter1(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
Deque<Object[]> stack = new ArrayDeque<>() {{
this.push(new Object[]{root, new ArrayList<>()});
}};
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Object[] objs = stack.pop();
TreeNode curr = (TreeNode) objs[0];
List<Integer> path = (List<Integer>) objs[1];
path.add(curr.val);
if (curr.left == null && curr.right == null) {
paths.add(path);
} else {
if (curr.right != null) {
stack.push(new Object[]{curr.right, new ArrayList<>(path)});
}
if (curr.left != null) {
stack.push(new Object[]{curr.left, path});
}
}
}
}
return paths.stream().anyMatch(p ->
p.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum() == targetSum
);
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface TriPredicate<A, B, C> {
boolean test(A a, B b, C c);
}
TriPredicate<TreeNode, Integer, Integer> recur2 = (root, sum, targetSum) -> {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
int currSum = sum + root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return currSum == targetSum;
} else if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {
return this.recur2.test(root.left, currSum, targetSum) || this.recur2.test(root.right, currSum, targetSum);
} else if (root.left != null) {
return this.recur2.test(root.left, currSum, targetSum);
} else {
return this.recur2.test(root.right, currSum, targetSum);
}
};
/**
* Accumulate val on each path and compare when reaching the leaf node
*/
boolean dfsRecur2(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
return this.recur2.test(root, 0, targetSum);
}
boolean dfsIter2(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root != null) {
Deque<Object[]> stack = new ArrayDeque<>() {{
this.push(new Object[]{root, 0});
}};
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Object[] objs = stack.pop();
TreeNode curr = (TreeNode) objs[0];
int sum = (int) objs[1];
int currSum = sum + curr.val;
if (curr.left == null && curr.right == null && currSum == targetSum) {
return true;
}
if (curr.right != null) {
stack.push(new Object[]{curr.right, currSum});
}
if (curr.left != null) {
stack.push(new Object[]{curr.left, currSum});
}
}
}
return false;
}Approach 2: Breadth-First Search
Rust
pub fn has_path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
//Self::bfs_iter_1(root, target_sum
Self::bfs_iter_2(root, target_sum)
}
///
/// 1. Find all the paths
/// 2. Compare the sum of one path with target_sum
///
fn bfs_iter_1(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
let mut paths = vec![];
if let Some(root) = root {
let mut queue = VecDeque::from([(root, vec![])]);
while let Some((curr, mut path)) = queue.pop_front() {
path.push(curr.borrow().val);
let left = curr.borrow_mut().left.take();
let right = curr.borrow_mut().right.take();
match (left, right) {
(None, None) => paths.push(path),
(left, right) => {
if let Some(left) = left {
queue.push_back((left, path.clone()));
}
if let Some(right) = right {
queue.push_back((right, path));
}
}
}
}
}
paths
.into_iter()
.any(|p| p.into_iter().sum::<i32>() == target_sum)
}
///
/// Accumulate val on each path and compare when reaching the leaf node
///
fn bfs_iter_2(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
if let Some(root) = root {
let mut queue = VecDeque::from([(root, 0)]);
while let Some((curr, sum)) = queue.pop_front() {
let curr_sum = curr.borrow().val + sum;
let left = curr.borrow_mut().left.take();
let right = curr.borrow_mut().right.take();
match (left, right) {
(None, None) => {
if curr_sum == target_sum {
return true;
}
}
(left, right) => {
if let Some(left) = left {
queue.push_back((left, curr_sum));
}
if let Some(right) = right {
queue.push_back((right, curr_sum));
}
}
}
}
}
false
}Java
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
//return bfsIter1(root, targetSum);
return this.bfsIter2(root, targetSum);
}
/**
* 1. Find all the paths
* 2. Compare the sum of one path with target_sum
*/
boolean bfsIter1(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
Deque<Object[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.addLast(new Object[]{root, new ArrayList<Integer>()});
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Object[] objs = queue.removeFirst();
TreeNode curr = (TreeNode) objs[0];
List<Integer> path = (List<Integer>) objs[1];
path.add(curr.val);
if (curr.left == null && curr.right == null) {
paths.add(path);
} else {
if (curr.left != null) {
queue.addLast(new Object[]{curr.left, new ArrayList<>(path)});
}
if (curr.right != null) {
queue.addLast(new Object[]{curr.right, path});
}
}
}
}
return paths.stream().anyMatch(p ->
p.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum() == targetSum
);
}
/**
* Accumulate val on each path and compare when reaching the leaf node
*/
boolean bfsIter2(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root != null) {
Deque<Object[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.addLast(new Object[]{root, 0});
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Object[] objs = queue.removeFirst();
TreeNode curr = (TreeNode) objs[0];
int sum = (int) objs[1];
int currSum = sum + curr.val;
if (curr.left == null && curr.right == null && currSum == targetSum) {
return true;
}
if (curr.left != null) {
queue.addLast(new Object[]{curr.left, currSum});
}
if (curr.right != null) {
queue.addLast(new Object[]{curr.right, currSum});
}
}
}
return false;
}